For those beginning to learn how to create code, these terms are often seen or spoken thus here is the meaning for better understanding of the topic
Computer science terms related to hardware
These computer science terms connect to the physical components of a computer. Hardware represents the most tactile aspects of computer science and the materials computers are made of.
1. CPU
CPU stands for the Central Processing Unit. It is the processing chip that serves as the "brains" of a device that interprets (or processes) the digital instructions provided by applications.
2. Bit
Bit is an abbreviation for “binary digit,” the smallest piece of information used by a computer. Each bit is either a 1 or a 0, which are the binary digits that make up computer language. Bits are literally the foundation upon which computer science is built. In modern computing, information is stored and processed at a scale that is orders of magnitude larger than individual bits. See the conversion rate below to better contextualize the size of a bit:
- 1 Byte = 8 bits
- 1 Kilobyte = 1,024 bytes
- 1 Megabyte = 1,024 kilobytes
- 1 Gigabyte = 1,024 megabytes
3. RAM
Random Access Memory (RAM) is the hardware component used to store data that is actively being used by a processor. When needed, information flows to RAM storage from long-term secondary storage—typically a hard drive.
4. Secondary storage
Secondary storage refers to the long-term data storage options found in a device. This includes hard disk drives (HDD) and solid-state drives (SSD). When you save a file to your computer, it is sent to secondary storage.
5. ROM
ROM stands for Read-Only Memory. This is memory that can only be read from and is not electronically modifiable after being manufactured. Computers use ROM to store critical foundational information like start-up processes and software instructions.
6. Input/Output Devices (I/O Devices)
I/O devices refer to anything people use to input information to the computer or to take information out (output). For example, a keyboard and mouse are input devices. A printer is an output device.
Computer science terms related to software
The physical components of devices are only the tip of the iceberg. Much of the computer science field focuses on software applications and their development.
7. Algorithm
At a basic level, algorithms are simply specific procedures used to solve computational problems. As computing power and data capabilities have grown more sophisticated, so have the algorithms and the problems they intend to solve. For example, a shipping company may turn to an algorithm to help determine the optimal route for delivery drivers.
8. API (Application Programming Interface)
An API is a software go-between that brings information from one application to another. It allows applications to communicate with one another while preserving some security measures for each end point. For example, an API can be used to securely transfer data stored by your web browser to a mobile app.
9. Boolean
A function in programming with binary choices, like “Yes or No” and “True or False.” This serves as a basic building block of programming logic.
10. Bug
A bug is a programming error that causes unexpected glitches or problems for a program’s end user. Debugging is the process of identifying, documenting and fixing the issues caused by bugs.
11. Camel Case
Camel case refers to the practice of capitalizing the first letter of each compound word in a programming variable to improve readability. For example, “StretchLength” and “FixedHeight.”
12. Code
Code refers to the string of commands or directions used by
different programming languages in order to create, edit or manage computer programs or applications. Code is used by computers to determine which action should be taken, define parameters and more.
13. Compiling
The process of taking code that’s written in a high-level language (like C++) by human developers and translating it into machine-readable code.
14. Conditional statements
Conditional statements, another fundamental piece of programming instructions, set the terms for when a program moves forward. This is often expressed in an “If, then” format. If all conditions expressed are met and true, only then will the computer move on to do the next step.
15. Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
An integrated development environment is a software tool where developers can write code and run their programs. Many provide useful features like syntax highlighting, debugging tools, version control and more.
16. Latency
Latency is the measure of time between entering an input and the returned output. The higher the latency, the longer it takes. This is an important factor for web applications and interfaces where a noticeable delay may impact user satisfaction.
17. Scripts
Similar in a way to the scripts used by Hollywood stars, a script in programming terms is a line by line set of instructions for a computer program to follow. These are often used for automation or for generating dynamic page content.
18. Structured data
This refers to data or information that’s been organized and “cleaned” in order to make it easier to search, manipulate and interface well with software applications. Structured data often is used for categories like names, addresses and credit card information but can be used for any quantifiable data category.
19. Syntax
Syntax refers to the rules that dictate the structure of a language. Programming languages, like all languages, need structure for the reader—whether a computer or a human—to make sense of the information. While some elements of syntax may carry over from language to language, most programming languages have unique and specific syntax rules that must be followed.
Computer science terms relating to the tech industry
Computer science today is about so much more than a computer and what it can do—it’s a massive area of study that intersects the industry of technology in countless ways. Here are some of the industry terms you’ll want to ensure you know.
20. Agile development
Agile development is a project management process for producing and releasing software (or other projects) that calls for quick cycles that repeat, improving as they go. This typically breaks projects down into smaller increments. This can be helpful in software development where the individual components of a software application may need to be adjusted or revised in order to accommodate unexpected issues or changes downstream.
21. Big data
Big data is a quick way to refer to the massive amounts of data collected by organizations on a day-to-day basis. Data at this scale can be tapped into for a variety of purposes like trend analyses, forecasting, process automation and more.
22. Cloud storage
Cloud storage is an alternative to storing data on a computer’s physical storage. Information stored “on the cloud” is kept on remote servers that can be accessed anywhere via the Internet. For more on how that works, check out
A Beginner’s Guide to Cloud Computing.
23. Cyber security
Cyber security is the process of protecting data from unauthorized users or hackers. It also represents a huge sector of the tech industry as more and more companies race to stay ahead of cyber criminals and security threats.
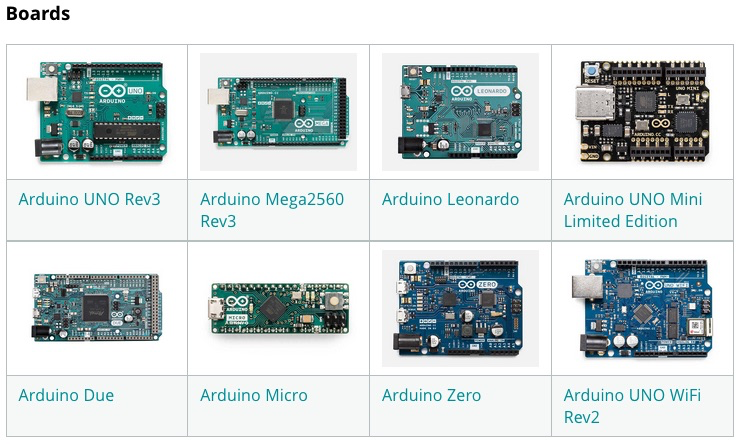
Arduino Terms
24. IDE Used in Arduino
Integrated Development Environment.
Includes the ability to create and edit program code then compile and load to an Arduino device
Within the environment common libraries are included with the ability to add custom designed libraries.
25. Function
Set of instructions performing a task
(In "C" the code is structured with sets of functions that is the program code)
26. Library library is a set of named functions that are included in C language to perform a specific function
27. Sketch the name that Arduino uses for a program code